Other heating/drying equipment Technical information
■What Are "Microwaves"?
"Microwaves" are a generic term for electromagnetic waves within the frequency range of 300 MHz to 30 GHz (wavelength 1 cm to 1 m). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency band are used in a variety of applications – microwave ovens in homes, industrial heating, cellular phones, UHF TV broadcasts, ship and airplane navigation, radar for weather observation, and aerospace communications.
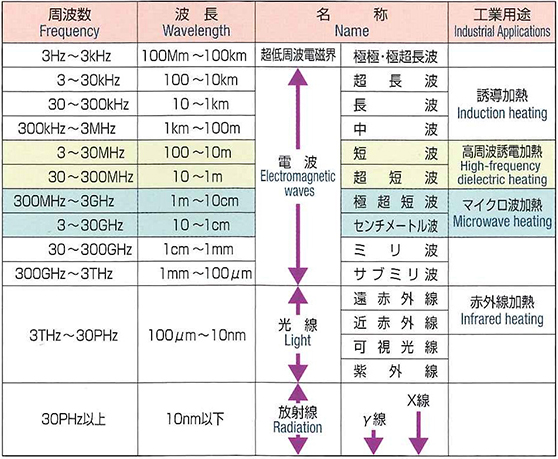
Kinds of Electromagnetic Waves
■Principle of Microwave Heating
When an electric field is applied to metal, for example, the flow of electrons (that is, current) does not occur when a so-called insulator is placed within that electrical field for an electric conductor having freely moving electrons. However, the phenomenon of polarization, where positive and minus electric charges are displaced from the equilibrium point, resulting in a separation of the charges, does occur. Substances with this kind of nature are called a "dielectric." As frequency increases, the component electrons of a dielectric spin, collide, vibrate, rub against each other, and otherwise move violently. Changes in polarity at this time are intense, occurring several ten to several hundred million times per second. This energy becomes "heat", which causes heat to be generated inside the dielectric.
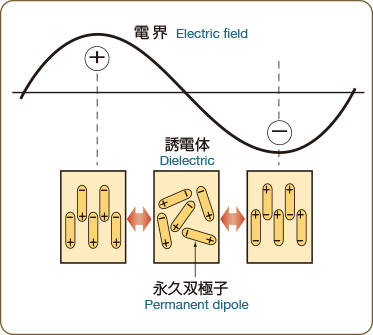
Electrical Field and Movement of Molecules in a Dielectric
■Various types of applicators
There are many different types of applicators for devices that apply microwaves. Select the optimum method best suited to the heated substance parameters, including the following:
- Shape (size, thickness)
- Electrical characteristics (specific conductivity), loss factor (εr・tan δ), water content
- State (liquid, solid, powder, etc.)
- Purpose (preheat, heat treatment, drying, bubbling, vulcanization, etc.)
- Treatment mode (fixed or continuous)
- Pressure control (vacuumed or pressurized)
-
Batch Type (Multimode)
The equipment is suited for heating wide or thick objects for a relatively long period of time.
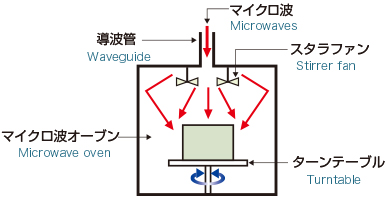
-
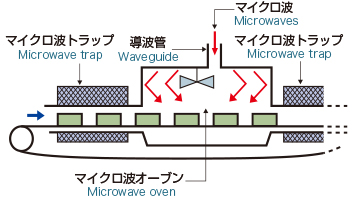
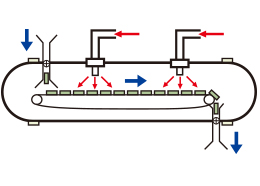
Conveyor Type (Multimode)
Objects are heated continuously while they are being transferred by a belt conveyor system. The equipment is designed to heat a large volume of objects.
-
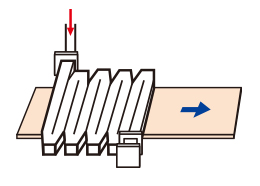
Waveguide Type (Singlemode)
The equipment is able to heat plates and sheets continuously.
-
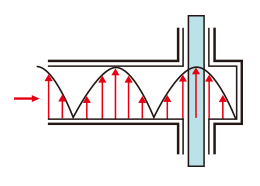
Standing-wave Type (Singlemode)
Objects are heated in an intense electric field generated in the waveguide by shortening the length of its tip.
-
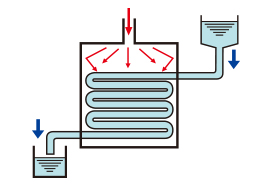
Liquid Pipeline Type
Liquid is continuously poured into pipes in the oven during heating treatment.
-
Vacuum / High-pressure Type
Objects placed in cans are heated in a vacuum or under high pressure.
-
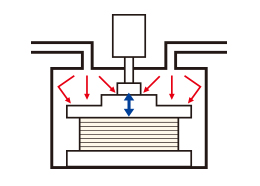
Press Type
Objects are pressed while they are being heated.
-
Mixing Type
Powdered and granular objects are mixed to be heated consistently.